How to fetch import cluster information?
TOC
Problem descriptionPrerequisitesGet cluster informationGet cluster tokenGet the import cluster API server address and CA certificateProblem description
Obtain the configuration required to connect to the import cluster so that the platform can be authorized to access and manage it. This section provides the steps to retrieve the import cluster information.
Prerequisites
-
A working
kubectlenvironment. For public cloud clusters, it is strongly recommended to use the provider's CloudShell. If CloudShell is not available, Linux or macOS is recommended. -
You have obtained the import cluster's KubeConfig file and copied it to the environment where
kubectlis installed. To avoid operating on the wrong environment, it is strongly recommended to use one of the following non-destructive approaches:- Backup approach: Copy your existing kubeconfig to a safe location first:
cp "${HOME}/.kube/config" "${HOME}/.kube/config.backup" - Isolated approach: Set the
KUBECONFIGenvironment variable to point to the imported kubeconfig:export KUBECONFIG="/path/to/imported/kubeconfig" - Merge approach: Use kubectl's merge/flatten without losing existing contexts:
export KUBECONFIG="/path/to/imported/kubeconfig:${HOME}/.kube/config"kubectl config view --flatten > "${HOME}/.kube/merged.kubeconfig"export KUBECONFIG="${HOME}/.kube/merged.kubeconfig"
- Backup approach: Copy your existing kubeconfig to a safe location first:
Get cluster information
Get cluster token
-
Run the following commands:
WARNINGThis procedure creates a cluster-admin credential intended to be non-expiring.
- Prefer least-privilege RBAC scoped to required resources if possible.
- Store the token securely; rotate/revoke when no longer needed.
- Limit who can read
Secretobjects incpaas-system.
-
An example of the token obtained in the previous step is shown below.
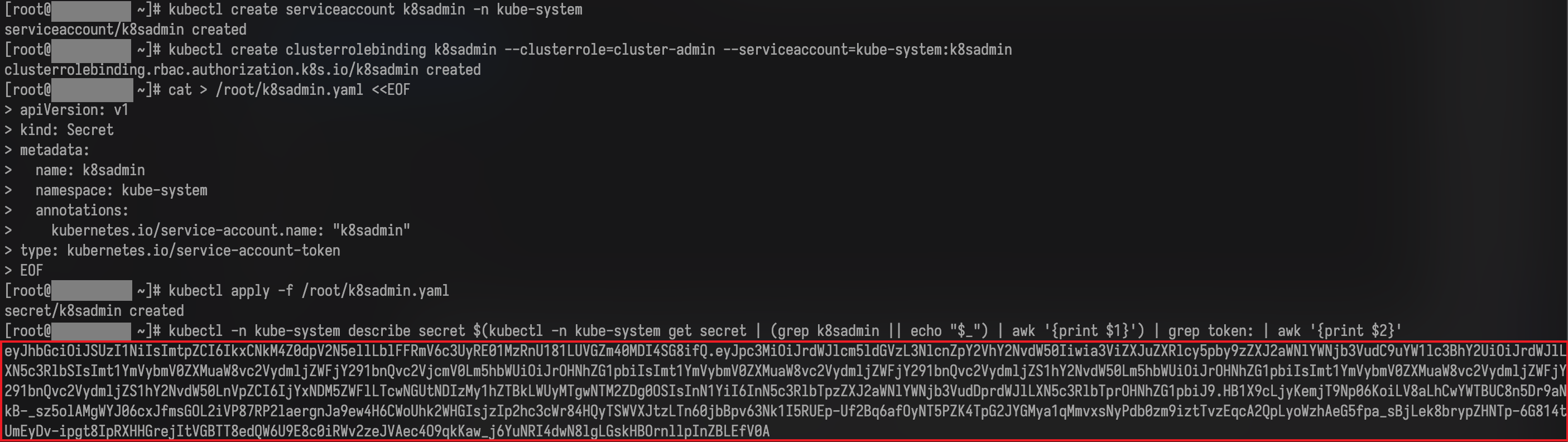
-
Validate the token expiration.
Use any tool that supports parsing JWT tokens to analyze the token and confirm its expiration time. If you can find an expiration field in the parsed result (a key containing "exp", as shown below), the platform will be unable to manage the import cluster after that time. In this case, stop and contact technical support.
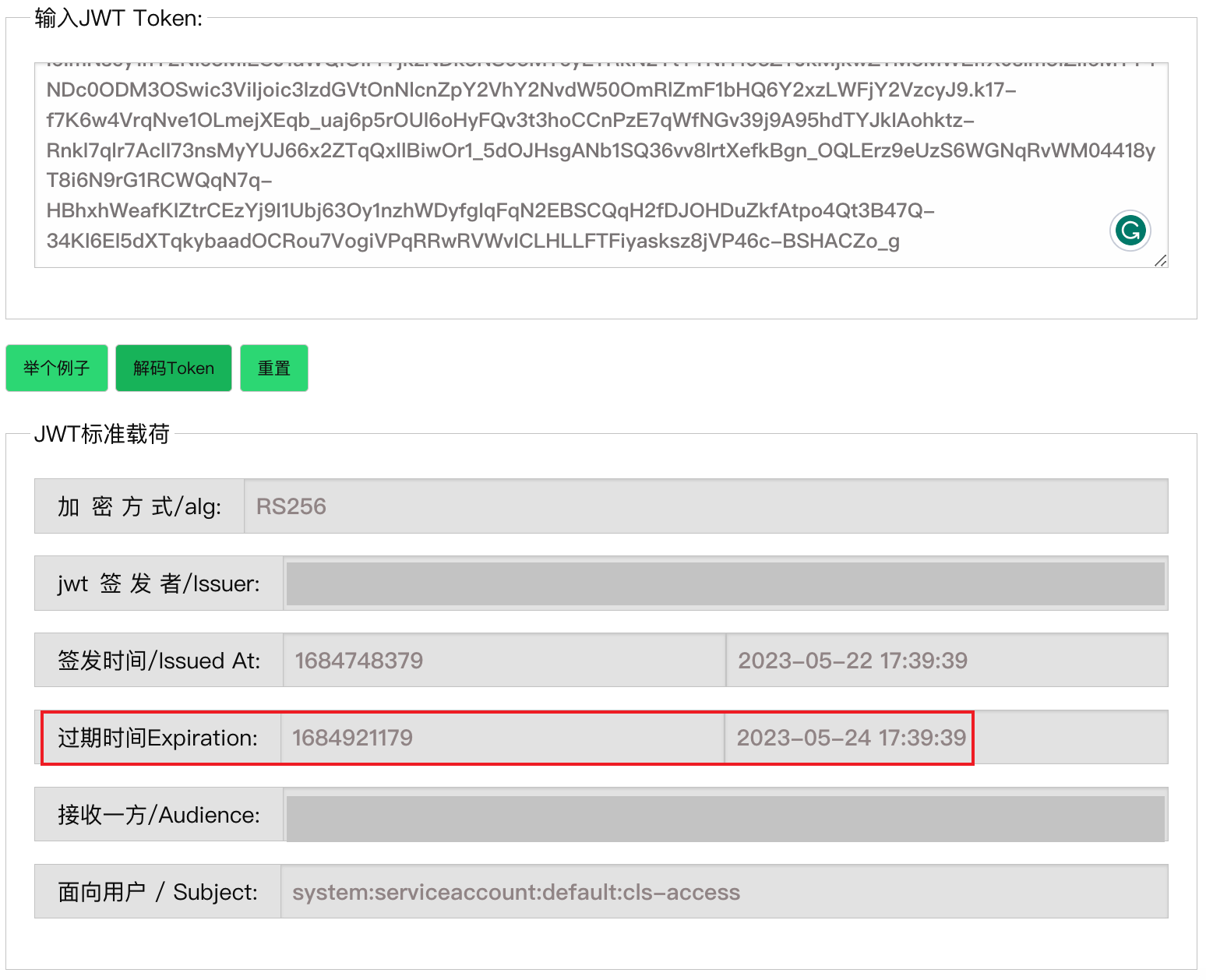
The expiration is recorded as "exp": 1684486916, in the original JWT payload. The value is a UNIX timestamp and can be converted to UTC time.
Cleanup (revoke access) when done:
Get the import cluster API server address and CA certificate
If you have already obtained the API server address and CA certificate using the platform's Parse KubeConfig File feature on the import cluster page, skip this step.
-
Run the following commands: