Architecture
Technical architecture
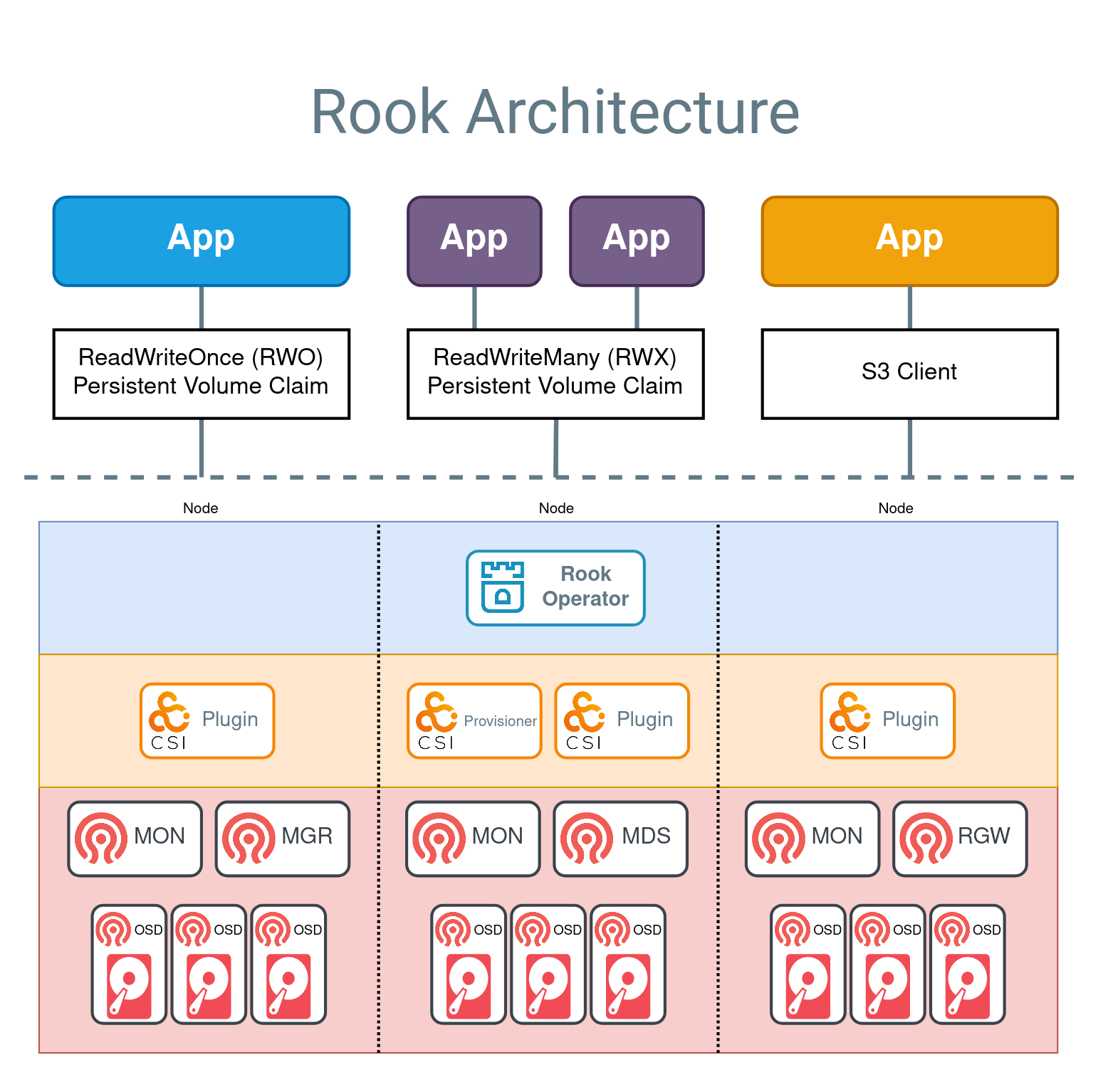
Example applications are shown above for the three supported storage types:
- Block Storage is represented with a blue app, which has a ReadWriteOnce (RWO) volume mounted. The application can read and write to the RWO volume, while Ceph manages the IO.
- Shared Filesystem is represented by two purple apps that are sharing a ReadWriteMany (RWX) volume. Both applications can actively read or write simultaneously to the volume. Ceph will ensure the data is safely protected for multiple writers with the MDS daemon.
- Object storage is represented by an orange app that can read and write to a bucket with a standard S3 client.
Below the dotted line in the above diagram, the components fall into three categories:
- Rook operator (blue layer): The operator automates configuration of Ceph
- CSI plugins and provisioners (orange layer): The Ceph-CSI driver provides the provisioning and mounting of volumes
- Ceph daemons (red layer): The Ceph daemons run the core storage architecture. See the Glossary to learn more about each daemon.
Block Storage
In the diagram above, the flow to create an application with an RWO volume is:
- The (blue) app creates a PVC to request storage.
- The PVC defines the Ceph RBD storage class (sc) for provisioning the storage.
- K8s calls the Ceph-CSI RBD provisioner to create the Ceph RBD image.
- The kubelet calls the CSI RBD volume plugin to mount the volume in the app.
- The volume is now available for reads and writes.
- A ReadWriteOnce volume can be mounted on one node at a time.
Shared Filesystem
In the diagram above, the flow to create a applications with a RWX volume is:
- The (purple) app creates a PVC to request storage.
- The PVC defines the CephFS storage class (sc) for provisioning the storage.
- K8s calls the Ceph-CSI CephFS provisioner to create the CephFS subvolume.
- The kubelet calls the CSI CephFS volume plugin to mount the volume in the app.
- The volume is now available for reads and writes.
- A ReadWriteMany volume can be mounted on multiple nodes for your application to use.
Object Storage S3
In the diagram above, the flow to create an application with access to an S3 bucket is:
- The (orange) app creates an BucketClaim to request a bucket.
- The Ceph COSI Driver creates a Ceph RGW bucket.
- The Ceph COSI Driver creates a secret with the credentials for accessing the bucket.
- The app retrieves the credentials from the secret.
- The app can now read and write to the bucket with an S3 client.