Configure a Dedicated Cluster for Distributed Storage
Dedicated cluster deployment refers to using an independent cluster to deploy the platform's distributed storage, where other business clusters within the platform access and utilize the storage services it provides through integration.
To ensure the performance and stability of the platform's distributed storage, only the platform's core components and distributed storage components are deployed in the dedicated storage cluster, avoiding the co-location of other business workloads. This separated deployment approach is the recommended best practice for the platform's distributed storage.
TOC
ArchitectureInfrastructure requirementsPlatform requirementsCluster requirementsResource requirementsStorage device requirementsStorage device type requirementsCapacity planningCapacity monitoring and expansionNetwork requirementsNetwork IsolationNetwork interface speed requirementsProcedureFollow-up ActionsArchitecture
Storage-Compute Separation Architecture
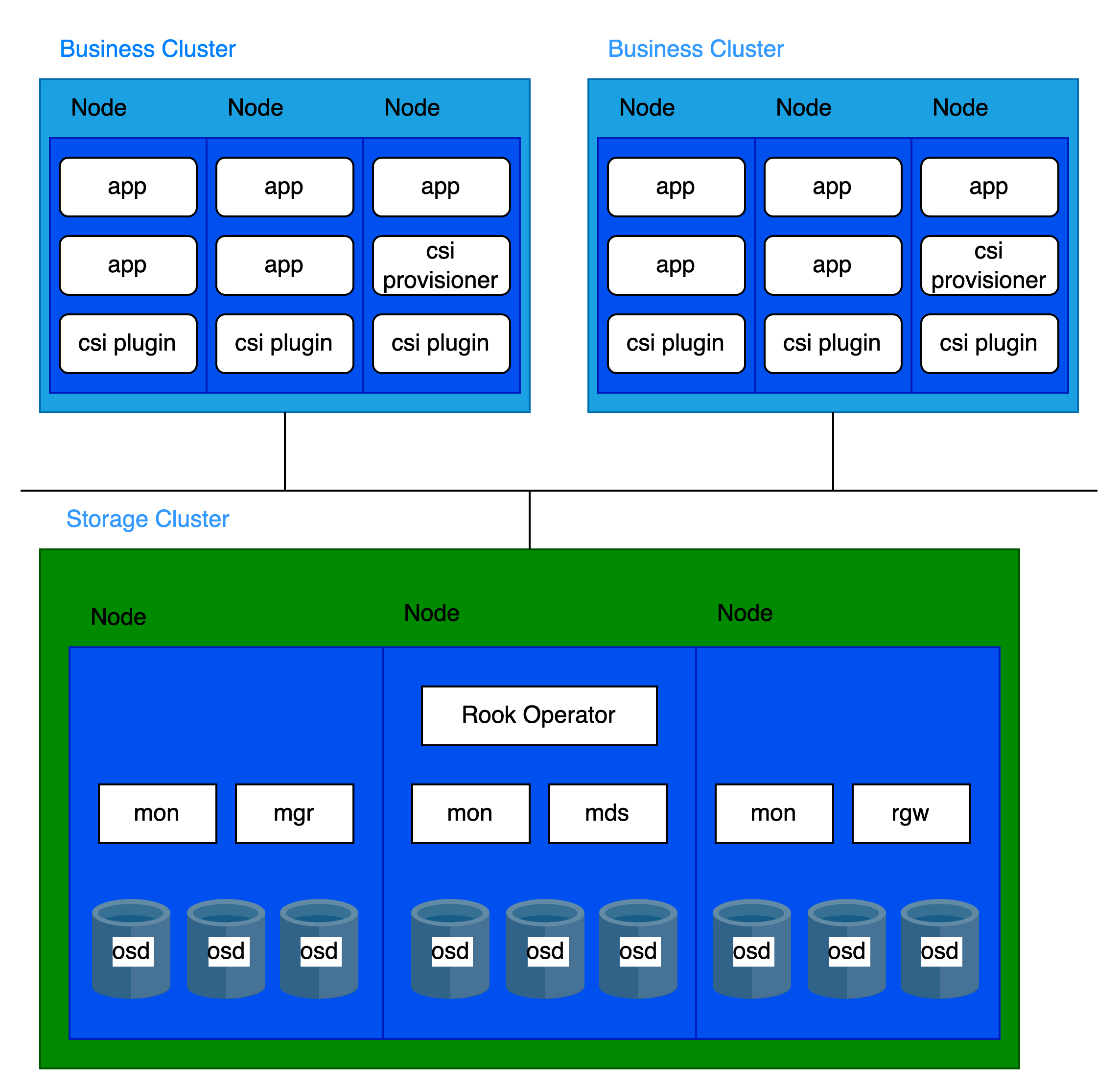
Infrastructure requirements
Platform requirements
Supported in version 3.18 and later.
Cluster requirements
It is recommended to use bare-metal clusters as dedicated storage clusters.
Resource requirements
Please refer to the Core Concepts for the components of distributed storage deployment.
Each component has distinct CPU and memory requirements. The recommended configurations are as follows:
A cluster typically runs:
- 3 MON
- 2 MGR
- multiple OSD
- 2 MDS (if using CephFS)
- 2 RGW (if using CephObjectStorage)
Based on the component distribution, the following per-node resource recommendations apply:
Storage device requirements
It is recommended to deploy 12 or fewer storage devices per node. This helps restrict the recovery time following a node failure.
Storage device type requirements
It is recommended to use enterprise SSDs with a capacity of 10TiB or smaller per device, and ensure all disks are identical in size and type.
Capacity planning
Before deployment, storage capacity must be planned according to specific business requirements. By default, the distributed storage system employs a 3-replica redundancy strategy. Therefore, the usable capacity is calculated by dividing the total raw storage capacity (from all storage devices) by 3.
Example for 30(N) nodes (replica count = 3), The usable capacity scenario is as follows:
Capacity monitoring and expansion
-
Proactive Capacity Planning
Always ensure usable storage capacity exceeds consumption. If storage is fully exhausted, recovery requires manual intervention and cannot be resolved by simply deleting or migrating data.
-
Capacity Alerts
The cluster triggers alerts at two thresholds:
- 80% utilization ("near full"): Proactively free up space or scale out the cluster.
- 95% utilization ("full"): Storage is fully exhausted, and standard commands cannot free space. Contact platform support immediately.
Always address alerts promptly and monitor storage usage regularly to avoid outages.
-
Scaling Recommendations
- Avoid: Adding storage devices to existing nodes.
- Recommended: Scale out by adding new storage nodes.
- Requirement: New nodes must use storage devices identical in size, type, and quantity to existing nodes.
Network requirements
Distributed storage must utilize HostNetwork.
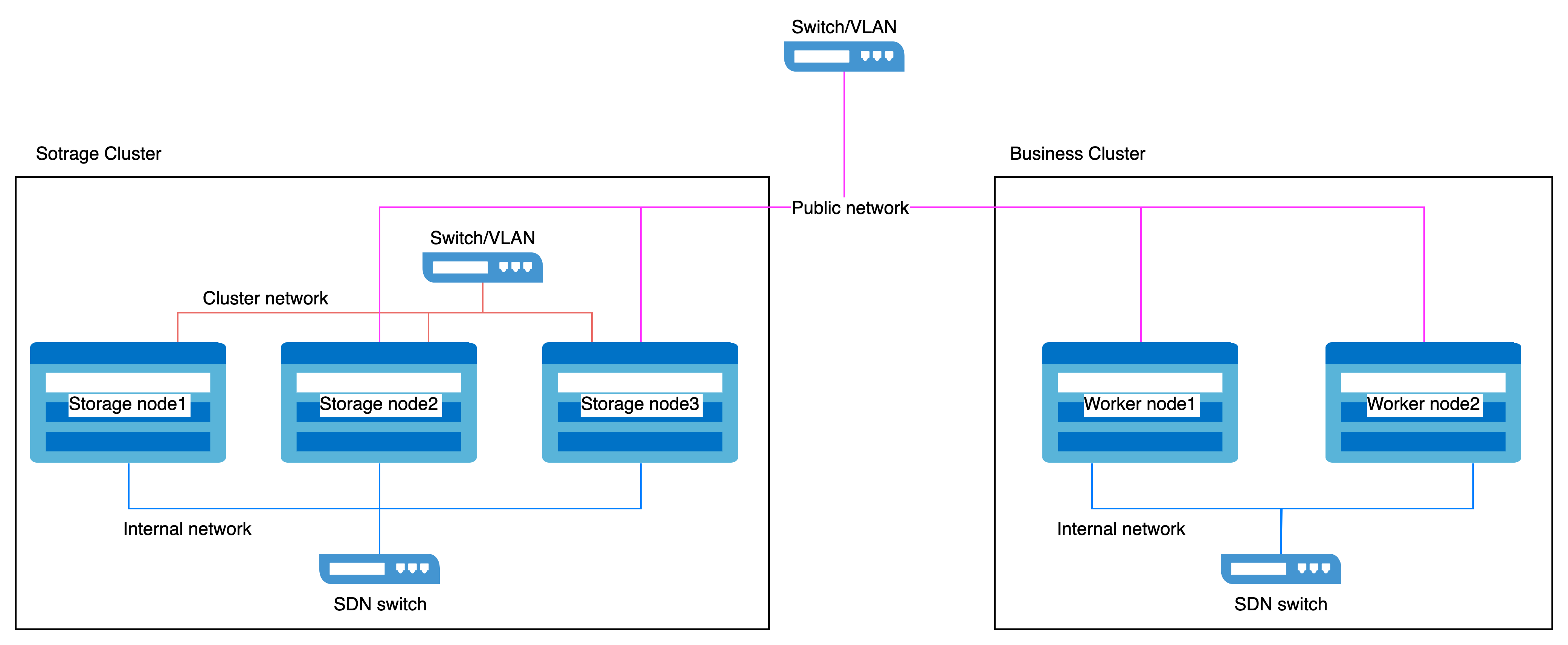
Network Isolation
The network is categorized into two types:
- Public Network: Used for client-to-storage component interactions (e.g., I/O requests).
- Cluster Network: Dedicated to data replication between replicas and data rebalancing (e.g., recovery).
To ensure service quality and performance stability:
- For Dedicated Storage Clusters:
Reserve two network interfaces on each host:- Public Network: For client and component communication.
- Cluster Network: For internal replication and rebalancing traffic.
- For Business Clusters:
Reserve one network interface on each host to access the storage Public Network.
Example Network Isolation Configuration
Network interface speed requirements
-
Storage Nodes
- Public Network and Cluster Network require 10GbE or higher network interfaces.
-
Business Cluster Nodes
- The network interface used to access the storage Public Network must be 10GbE or higher.
Procedure
Deploy Operator
-
Access Platform Management.
-
In the left sidebar, click Storage Management > Distributed Storage.
-
Click Create Now.
-
In the Deploy Operator wizard page, click the Deploy Operator button at the bottom right.
- When the page automatically advances to the next step, it indicates that the Operator has been deployed successfully.
- If the deployment fails, please refer to the prompt on the interface Clean Up Deployed Information and Retry, and redeploy the Operator; if you wish to return to the distributed storage selection page, click Application Store, first uninstall the resources in the already deployed rook-operator, and then uninstall rook-operator.
Create ceph cluster
Execute commands on the control node of the storage cluster.
Click to view
Parameters:
- public network cidr: CIDR of the storage Public Network (e.g.,
- 10.0.1.0/24). - cluster network cidr: CIDR of the storage Cluster Network (e.g.,
- 10.0.2.0/24). - storage devices: Specify the storage devices to be utilized by the distributed storage.
Example Formatting:TipUses the disk's World Wide Name (WWN) for stable naming, which avoids reliance on volatile device paths like
sdbthat may change after reboots.
Create storage pools
Three storage pool types are available. Select and create the appropriate ones based on your business requirements.
Create file pool
Execute commands on the control node of the storage cluster.
Click to view
Create block pool
Execute commands on the control node of the storage cluster.
Click to view
Create object pool
Execute commands on the control node of the storage cluster.
Click to view
Follow-up Actions
When other clusters need to utilize the distributed storage service, refer to the following guidelines.
Accessing Storage Services