CUDA Driver and Runtime Compatibility
TOC
Hierarchical Architecture & Core Concepts1. CUDA Runtime API LayerTechnical PositioningVersion Detection Methods2. CUDA Driver API LayerTechnical PositioningVersion Detection MethodsVersion Compatibility Matrix & ConstraintsPhysical GPU Deployment - Core Compatibility PrinciplesFormal RulesVirtualization Scenario Enhancements (HAMI/GPU-Manager)Version RequirementsDeployment Best PracticesRecommended StrategyAlternative Solutions for Legacy Systems1. Physical GPU Scheduling or GPU-Manager Whole-Card Allocation2. Node Labeling Strategy3. Runtime Version UpgradeTroubleshooting HandbookCommon Error CodesHierarchical Architecture & Core Concepts
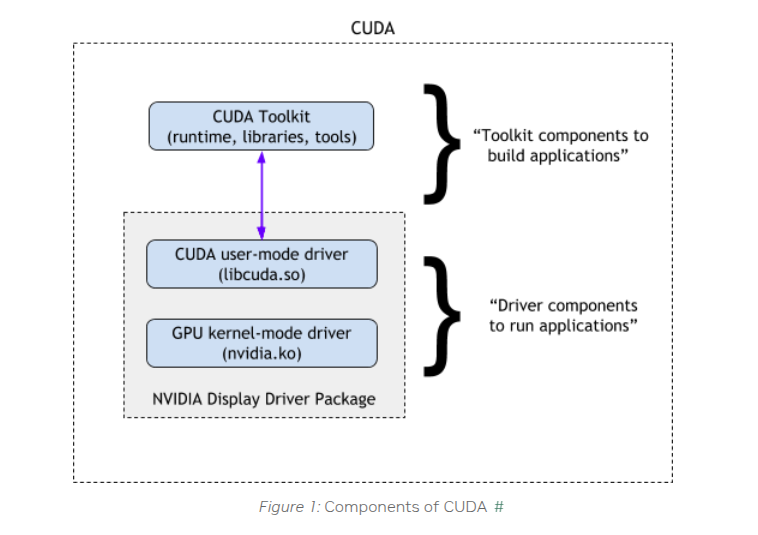
1. CUDA Runtime API Layer
Technical Positioning
- Functional Scope: Provides high-level abstraction interfaces for developers, encapsulating core GPU operations (memory allocation, stream management, kernel launches, etc.)
- Version Binding: Determined by the CUDA Toolkit version used during build (e.g., CUDA 12.0.1)
Version Detection Methods
if you find multi lib version, you should check your program which version used,like PATH, LD_LIBRARY_PATH or other program set
2. CUDA Driver API Layer
Technical Positioning
- Functional Scope: Low-level interface directly interacting with GPU hardware, handling instruction translation and hardware resource scheduling
- Version Binding: Determined by NVIDIA driver version, following SemVer specification
Version Detection Methods
Version Compatibility Matrix & Constraints
Physical GPU Deployment - Core Compatibility Principles
First reference NVIDIA's official statement,the base constraints is
- Driver version must always be ≥ Runtime version
- NVIDIA officially guarantees 1 major version backward compatibility (e.g., CUDA Driver 12.x supports Runtime 11.x)
- Cross-two-major-version compatibility (e.g., Driver 12.x with Runtime 10.x) is neither officially supported nor recommended
when you deploy cuda program,please comply with the base constraints
Formal Rules
Virtualization Scenario Enhancements (HAMI/GPU-Manager)
When using Virtual GPU solutions like GPU-Manager or HAMI, besides the base constraints up, you must comply with the additional constraints apply:
Version Requirements
Special Note for GPU-Manager: We implemented partial cross-1-major-version compatibility (e.g., baseline 12.4 supporting vLLM 11.8). However, this requires per-application hook adjustments and must be analyzed case-by-case.
Deployment Best Practices
Recommended Strategy
• Adopt newer CUDA versions (e.g., CUDA 12.x) for both Driver and Runtime in new GPU cluster planning
Alternative Solutions for Legacy Systems
1. Physical GPU Scheduling or GPU-Manager Whole-Card Allocation
Whole-card scheduling provides native compatibility equivalent to physical GPU access GPU-Manager can use whole card mode when you set tencent.com/vcuda-core to 100 multily positive integer,like 100,200,300
2. Node Labeling Strategy
Label nodes based on supported Driver CUDA versions:
this means your node is cuda 12.4
Configure scheduling affinity in deployments: you can set cuda-major-version and cuda-minor-version by your program cuda runtime need
3. Runtime Version Upgrade
Legacy CUDA Runtimes may have security vulnerabilities (CVEs) and lack support for new GPU features. Prioritize upgrades to CUDA 12.x.
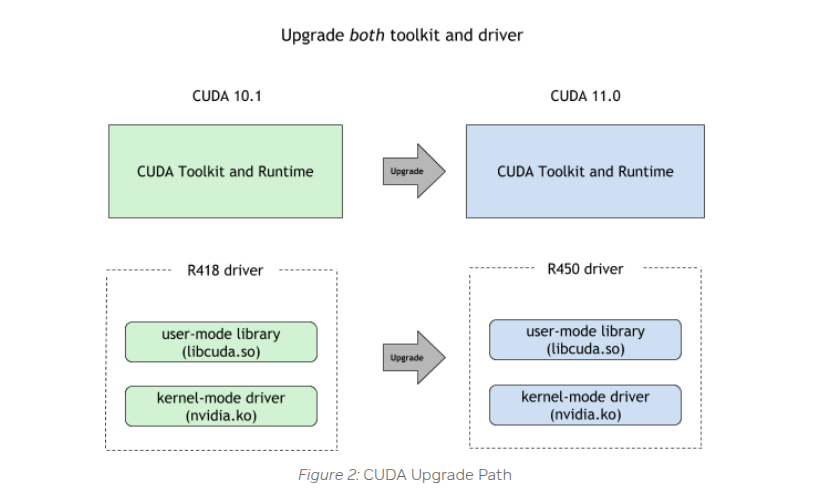
nvidia recomend to upgrade both