Creating Ingresses
Ingress rules (Kubernetes Ingress) expose HTTP/HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to internal routing (Kubernetes Service), enabling control of external access to computing components.
Create an Ingress to manage the external HTTP/HTTPS access to a Service.
When creating multiple ingresses within the same namespace, different ingresses MUST NOT have the same Domain, Protocol, and Path (i.e., duplicate access points are not allowed).
TOC
Implementation Method
Ingress rules depend on the implementation of the Ingress Controller, which is responsible for listening to changes in Ingress and Service. After a new Ingress rule is created, a forwarding rule matching the Ingress rule is automatically generated within the Ingress Controller. When the Ingress Controller receives a request, it matches the forwarding rule from the Ingress rule and distributes the traffic to the specified internal routes, as shown in the diagram below.
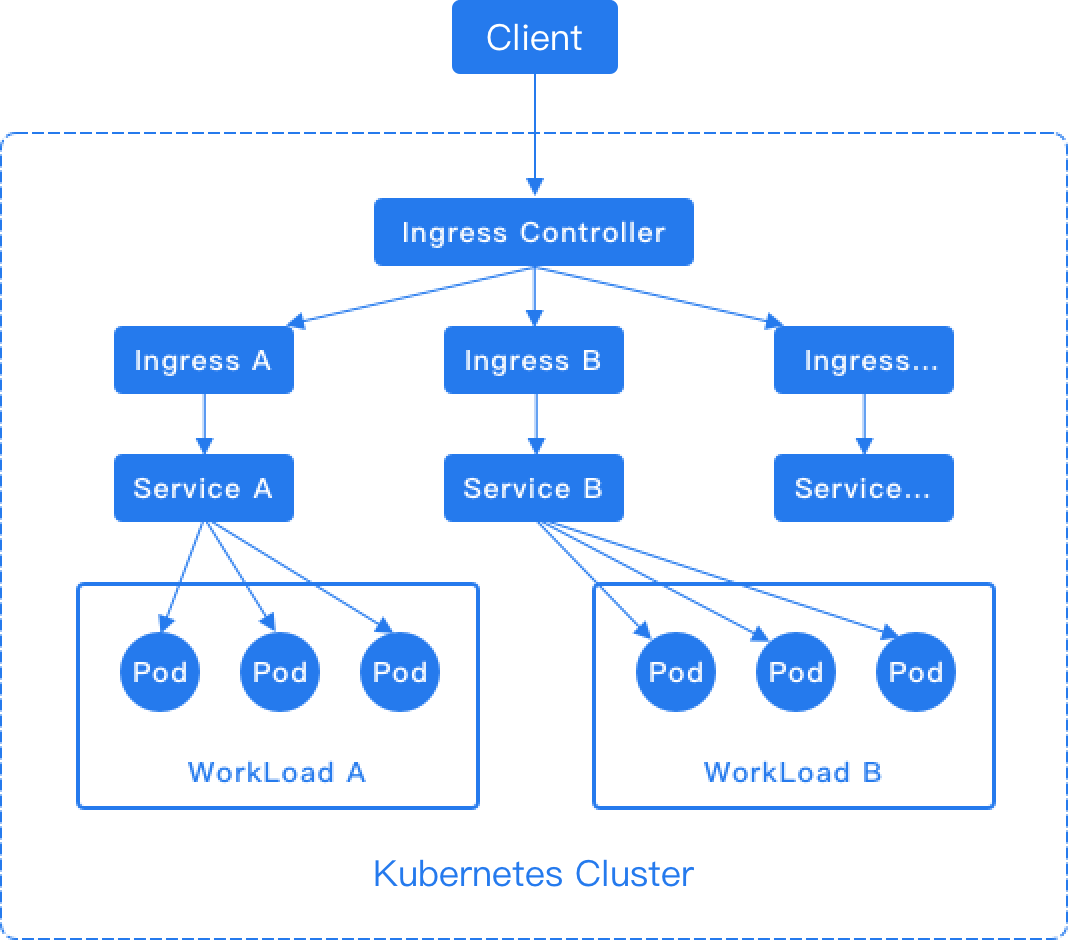
For the HTTP protocol, Ingress only supports the 80 port as the external port. For the HTTPS protocol, Ingress only supports the 443 port as the external port. The platform's load balancer will automatically add the 80 and 443 listening ports.
Quick Start
Next, we will use the community version of Ingress-NGINX to demonstrate how to access your own application using the NGINX controller.
-
deploy
Ingress-NGINXcontroller.The following resources are automatically created after using this command:
If you want to change the default registry address, you can use
curlto download the YAML file, change it, and then apply the YAML file.Waiting for the
ingress-nginx-controller-xxxPod to run -
Local testing
-
Creating a simple web server and the associated service:
-
Creating an ingress resource. This example uses a host that maps to
localhost: -
Forward a local port to the ingress controller:
-
Accessing your deployment using curl:
Note: This parameter temporarily resolves the domain name demo.local to IP 127.0.0.1 and is used on port 8080. When you visit http://demo.local:8080, you are actually visiting http://127.0.0.1:8080. On the other hand, you should configure
hosts:Final you should see a HTML response containing text like "Welcome to nginx!".
Then you can access website
http://demo.local:8080/.
INFOingress-nginx-controllerdefault type isLoadBalancer, IfEXTERNAL-IPfield showspending, this means that your Kubernetes cluster wasn't able to provision the load balancer.If you're integrating with a provider that supports specifying the load balancer IP address(es) for a Service via a (provider specific) annotations, you should switch to doing that.
-
-
Online testing
When your
ingress-nginx-controller(Service of LoadBalancer type) exists anEXTERNAL-IP, Then you can create an ingress resource. The following example assumes that you have set up a DNS record forwww.developer.io:You can access
http://www.developer.ioto see the same output.
Prerequisites
-
There must be an available Service in the current namespace.
-
Please confirm with the administrator that a usable domain name has been allocated for the project associated with the current namespace.
-
To access the domain via HTTPS, you need to first save the HTTPS certificate as a TLS secret.
Example Ingress:
- To see more configurations please refer to nginx-configuration.
- Using
ingress-nginxcontroller. - If you only want to run ingress locally, configure the
hostsbeforehand.
Creating a Ingress by using the web console
-
Access the Container Platform.
-
In the left navigation bar, click Network > Ingress.
-
Click Create Ingress.
-
Reference the instructions below to configure certain parameters.
-
Click Create.
Creating a Ingress by using the CLI
If the ingress has no Ingress Class, all the ALB instances that are allocated to this project will handle this ingress.