OTel
OpenTelemetry (OTel) is an open-source project aimed at providing a vendor-neutral standard for collecting, processing, and exporting telemetry data in distributed systems, such as microservices architectures. It helps developers analyze the performance and behavior of software more easily, thus facilitating the diagnosis and resolution of application issues.
TOC
Terminology
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Trace | The data submitted to the OTel Server, which is a collection of related events or operations used to track the flow of requests in distributed systems; each Trace consists of multiple Spans. |
| Span | An independent operation or event within a Trace that includes start time, duration, and other relevant information. |
| OTel Server | An OTel server capable of receiving and storing Trace data, such as Jaeger, Prometheus, etc. |
| Jaeger | An open-source distributed tracing system used for monitoring and troubleshooting microservices architectures, supporting integration with OpenTelemetry. |
| Attributes | Key-value pairs attached to a Trace or Span to provide additional contextual information. This includes Resource Attributes and Span Attributes; see Attributes for more information. |
| Sampler | A strategy component that determines whether to sample and report a Trace. Different sampling strategies can be configured, such as full sampling, proportional sampling, etc. |
| ALB (Another Load Balancer) | A software or hardware device that distributes network requests across available nodes in a cluster; the load balancer (ALB) used in the platform is a layer 7 software load balancer, which can be configured to monitor traffic with OTel. ALB supports submitting Traces to a specified Collector and allows different sampling strategies; it also supports configuring whether to submit Traces at the Ingress level. |
| FT (Frontend) | The port configuration for ALB, specifying port-level configurations. |
| Rule | Routing rules on the port (FT) used to match specific routes. |
| HotROD (Rides on Demand) | A sample application provided by Jaeger to demonstrate the use of distributed tracing; refer to Hot R.O.D. - Rides on Demand for more details. |
| hotrod-with-proxy | Specifies the addresses of HotROD's internal microservices via environment variables; refer to hotrod-with-proxy for more details. |
Prerequisites
-
Ensure that an operable ALB exists: Create or use an existing ALB, where the name of the ALB is replaced with
<otel-alb>in this document. For instructions on creating an ALB, refer to Creating Load Balancer. -
Ensure that there is an OTel data reporting server address: This address will hereinafter be referred to as
<jaeger-server>.
Procedure
Update ALB Configuration
-
On the Master node of the cluster, use the CLI tool to execute the following command to edit the ALB configuration.
-
Add the following fields under the
spec.configsection.Example configuration once completed:
-
Execute the following command to save the updates. After the update, the ALB will default to enabling OpenTelemetry, and all request Trace information will be reported to the Jaeger Server.
Related Operations
Configuring OTel in Ingress
-
Enable or Disable OTel on Ingress
By configuring whether to enable OTel on Ingress, you can better monitor and debug the request flow of applications, identifying performance bottlenecks or errors by tracing requests as they propagate between different services.
Procedure
Add the following configuration under the metadata.annotations field of Ingress:
Parameter Explanation:
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-opentelemetry: When set to
true, it indicates that the Ingress controller enables OpenTelemetry functionality while processing requests through this Ingress, which means request Trace information will be collected and reported. When set tofalseor this annotation is removed, it means that request Trace information will not be collected or reported.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-opentelemetry: When set to
-
Enable or Disable OTel Trust on Ingress
OTel Trust determines whether Ingress trusts and uses the Trace information (e.g., trace ID) from incoming requests.
Procedure
Add the following configuration under the metadata.annotations field of Ingress:
Parameter Explanation:
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/opentelemetry-trust-incoming-span: When set to
true, the Ingress continues to use already existing Trace information, helping maintain consistency in cross-service tracing, allowing the entire request chain to be fully traced and analyzed in the distributed tracing system. When set tofalse, it will generate new tracing information for the request, which may cause the request to be treated as part of a new tracing chain after entering the Ingress, interrupting cross-service trace continuity.
- nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/opentelemetry-trust-incoming-span: When set to
-
Add Different OTel Configurations on Ingress
This configuration allows you to customize OTel's behavior and data export methodology for different Ingress resources, enabling fine-grained control over each service's tracing strategy or target.
Procedure
Add the following configuration under the metadata.annotations field of Ingress:
Parameter Explanation:
- exporter: Specifies how the collected Trace data is sent to the OTel Collector (the OTel data reporting server).
- address: Specifies the address of the OTel Collector.
- request_timeout: Specifies the request timeout.
Using OTel in Applications
The following configuration shows the complete OTel configuration structure, which can be used to define how to enable and use OTel features in applications.
On the cluster Master node, use the CLI tool to execute the following command to get the complete OTel configuration structure.
Echoed Result:
Parameter Explanation:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| otel.enable | Whether to enable OTel functionality. |
| exporter.collector.address | The address of the OTel data reporting server, supporting http/https protocols and domain names. |
| flags.hide_upstream_attrs | Whether to report information about upstream rules. |
| flag.notrust_incoming_span | Whether to trust and use the OTel Trace information (e.g., trace ID) from incoming requests. |
| flags.report_http_request_header | Whether to report request headers. |
| flags.report_http_response_header | Whether to report response headers. |
| sampler.name | Sampling strategy name; see Sampling Strategies for details. |
| sampler.options.fraction | Sampling rate. |
| sampler.options.parent_name | The parent strategy for parent_base sampling strategies. |
Inheritance
By default, if the ALB configures certain OTel parameters and FT is not configured, FT will inherit the parameters from the ALB as its own configuration; that is, FT inherits the ALB configuration, while Rule can inherit configurations from both ALB and FT.
-
ALB: The configuration on the ALB is typically global and default. You can configure global parameters such as Collector addresses here, which will be inherited by the lower-level FT and Rule.
-
FT: FT can inherit configurations from ALB, meaning that certain OTel parameters that are not configured on FT will use the configuration from ALB. However, FT can also be refined further; for instance, you can choose to selectively enable or disable OTel on FT without affecting other FT or the global settings of ALB.
-
Rule: Rule can inherit configurations from both ALB and FT. However, Rule can also be refined further; for instance, a specific Rule can choose not to trust the incoming OTel Trace information or to adjust the sampling strategies.
Procedure
By configuring the spec.config.otel field in the YAML files of ALB, FT, and Rule, you can add OTel-related configuration.
Additional Notes
Sampling Strategies
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| always on | Always report all tracing data. |
| always off | Never report tracing data. |
| traceid-ratio | Decide whether to report based on traceid. The format of traceparent is xx-traceid-xx-flag, where the first 16 characters of traceid represent a 32-bit hexadecimal integer. If this integer is less than fraction multiplied by 4294967295 (i.e., (2^32-1)), it will be reported. |
| parent-base | Decide whether to report based on the flag part of the traceparent in the request. When the flag is 01, it will be reported; for example: curl -v "http://$ALB_IP/" -H 'traceparent: 00-xx-xx-01'; when the flag is 02, it will not be reported; for example: curl -v "http://$ALB_IP/" -H 'traceparent: 00-xx-xx-02'. |
Attributes
-
Resource Attributes
These attributes are reported by default.
Parameter Description hostname The hostname of the ALB Pod service.name The name of the ALB service.namespace The namespace where the ALB resides service.type Default is ALB service.instance.id The name of the ALB Pod -
Span Attributes
-
Attributes reported by default:
Parameter Description http.status_code Status code http.request.resend_count Retry count alb.rule.rule_name The name of the rule matched by this request alb.rule.source_type The type of the rule matched by this request, currently only Ingress alb.rule.source_name The name of the Ingress alb.rule.source_ns The namespace where the Ingress resides -
Attributes reported by default but can be excluded by modifying the flag.hide_upstream_attrs field:
Parameter Description alb.upstream.svc_name The name of the Service (internal route) to which traffic is forwarded alb.upstream.svc_ns The namespace where the Service (internal route) being forwarded resides alb.upstream.peer The IP address and port of the Pod being forwarded to -
Attributes not reported by default but can be reported by modifying the flag.report_http_request_header field:
Parameter Description **http.request.header.<header>**Request Header -
Attributes not reported by default but can be reported by modifying the flag.report_http_response_header field:
Parameter Description **http.response.header.<header>**Response Header
-
Configuration Example
The following YAML configuration deploys an ALB and uses Jaeger as the OTel server, with Hotrod-proxy as the demonstration backend. By configuring Ingress rules, when clients request the ALB, the traffic will be forwarded to HotROD. Additionally, the communication between internal microservices of HotROD is also routed through the ALB.
-
Save the following YAML as a file named all.yaml.
-
In the CLI tool, execute the following command to deploy Jaeger, ALB, HotROD, and all necessary CRs for testing.
-
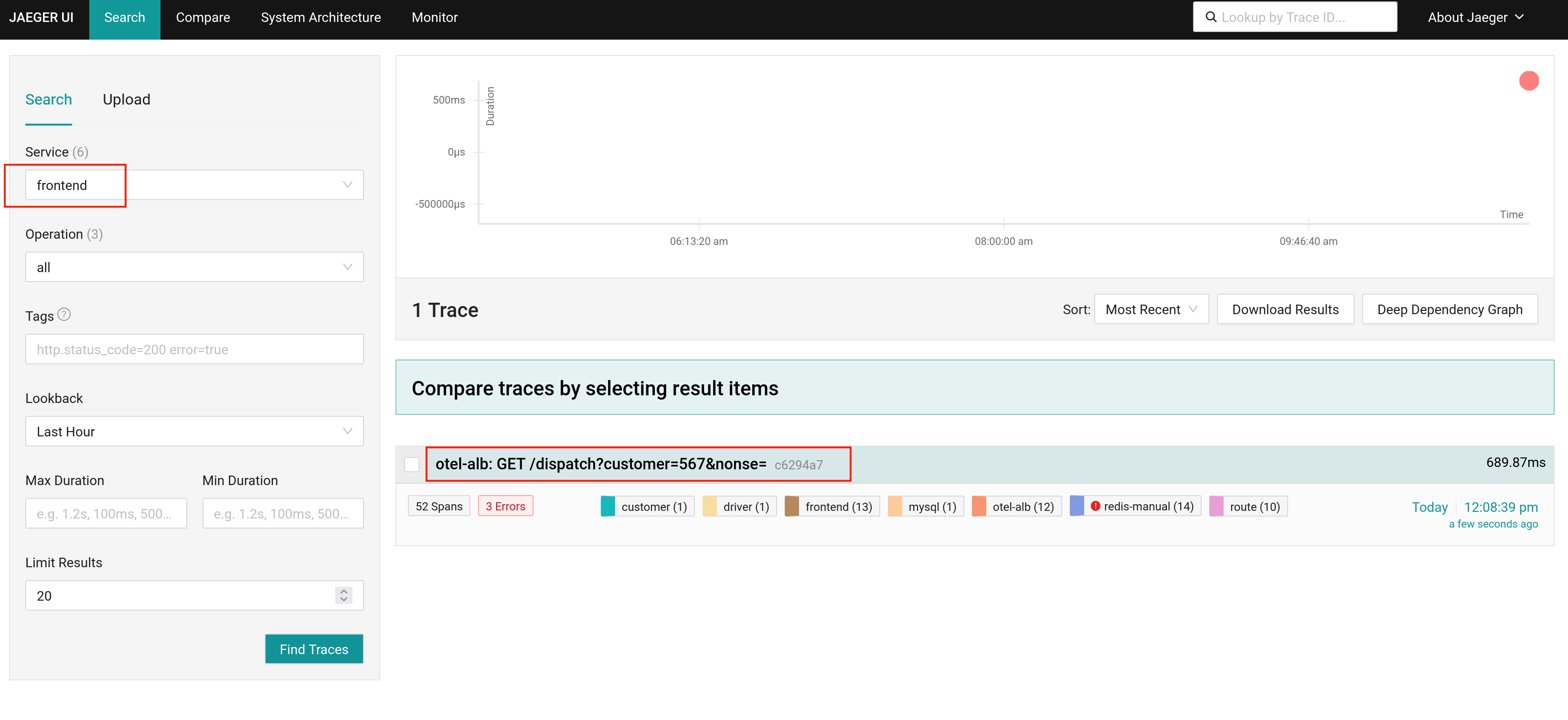
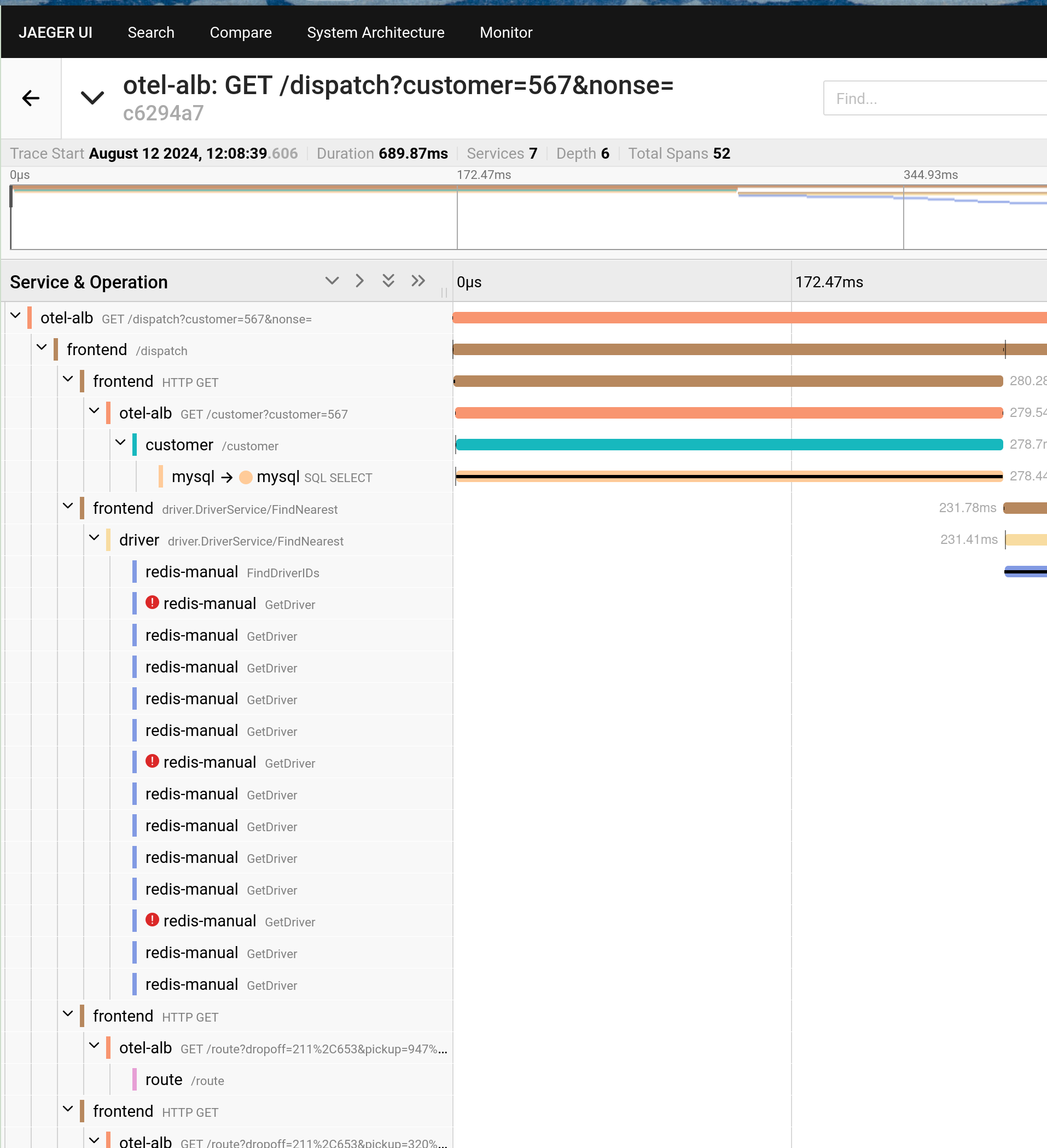
Execute the following command to get the access address of Jaeger.
-
Execute the following command to obtain the access address of otel-alb.
-
Execute the following command to send a request to HotROD via ALB. Here, ALB will report the Trace to Jaeger.
-
Open the access address of Jaeger obtained in Step 3 to view the results.