TOC
About Egress Gateway
Egress Gateway is used to control external network access for Pods with a group of static addresses and has the following features:
- Achieves Active-Active high availability through ECMP, enabling horizontal throughput scaling
- Implements fast failover (<1s) via BFD
- Supports IPv6 and dual-stack
- Enables granular routing control through NamespaceSelector and PodSelector
- Allows flexible scheduling of Egress Gateway through NodeSelector
At the same time, Egress Gateway has the following limitations:
- Uses macvlan for underlying network connectivity, requiring Underlay support from the underlying network
- In multi-instance Gateway mode, multiple Egress IPs are required
- Currently, only supports SNAT; EIP and DNAT are not supported
- Currently, recording source address translation relationships is not supported
Implementation Details
Each Egress Gateway consists of multiple Pods with multiple network interfaces.
Each Pod has two network interfaces: one joins the virtual network for communication within the VPC,
and the other connects to the underlying physical network via Macvlan for external network communication.
Virtual network traffic ultimately accesses the external network through NAT within the Egress Gateway instances.
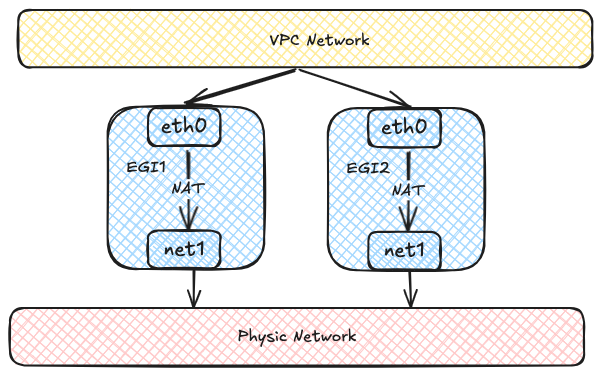
Each Egress Gateway instance registers its address in the OVN routing table.
When a Pod within the VPC needs to access the external network,
OVN uses source address hashing to forward traffic to multiple Egress Gateway instance addresses,
achieving load balancing. As the number of Egress Gateway instances increases,
throughput can also scale horizontally.
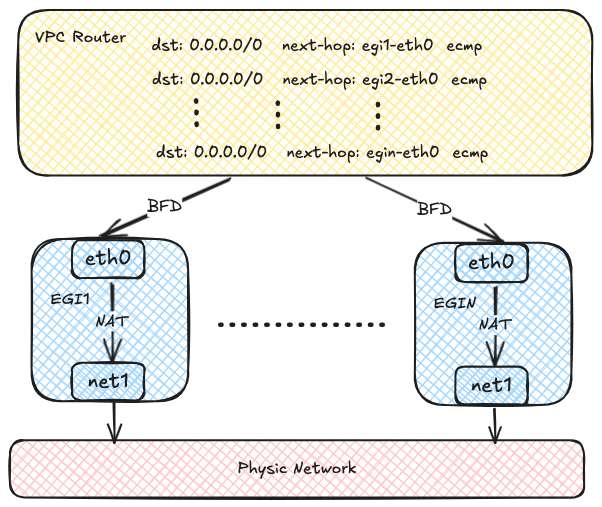
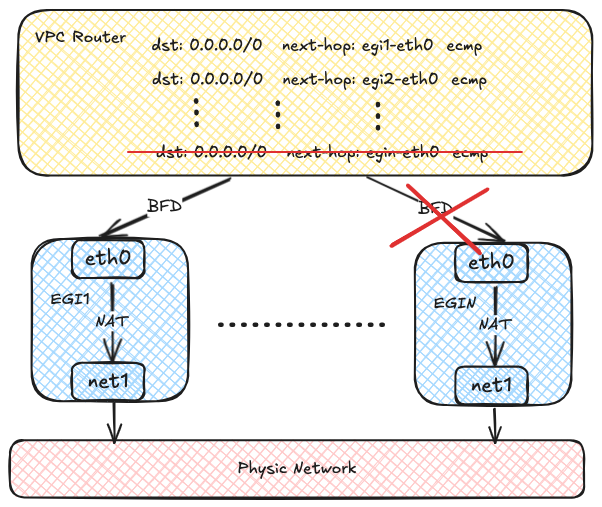
OVN uses the BFD protocol to probe multiple Egress Gateway instances.
When an Egress Gateway instance fails, OVN marks the corresponding route as unavailable,
enabling rapid failure detection and recovery.
Notes
- Only Kube-OVN CNI supports Egress Gateway.
- Egress Gateway requires Multus-CNI.
Usage
Creating a Network Attachment Definition
Egress Gateway uses multiple NICs to access both the internal network and the external network,
so you need to create a Network Attachment Definition to connect to the external network.
An example of using the macvlan plugin with IPAM provided by Kube-OVN is shown below:
apiVersion: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1
kind: NetworkAttachmentDefinition
metadata:
name: eth1
namespace: default
spec:
config: '{
"cniVersion": "0.3.0",
"type": "macvlan",
"master": "eth1",
"mode": "bridge",
"ipam": {
"type": "kube-ovn",
"server_socket": "/run/openvswitch/kube-ovn-daemon.sock",
"provider": "eth1.default"
}
}'
---
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: Subnet
metadata:
name: macvlan1
spec:
protocol: IPv4
provider: eth1.default
cidrBlock: 172.17.0.0/16
gateway: 172.17.0.1
excludeIps:
- 172.17.0.2..172.17.0.10
- Host interface that connects to the external network.
- Provider name with a format of
<network attachment definition name>.<namespace>.
- Provider name used to identify the external network and MUST be consistent with the one in the NetworkAttachmentDefinition.
TIP
You can create a Network Attachment Definition with any CNI plugin to access the corresponding network.
Creating a VPC Egress Gateway
Create a VPC Egress Gateway resource as shown in the example below:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: VpcEgressGateway
metadata:
name: gateway1
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
externalSubnet: macvlan1
nodeSelector:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- kube-ovn-worker
- kube-ovn-worker2
selectors:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: default
policies:
- snat: true
subnets:
- subnet1
- snat: false
ipBlocks:
- 10.18.0.0/16
- Namespace where the VPC Egress Gateway instances is created.
- Replicas of the VPC Egress Gateway instances.
- External subnet that connects to the external network.
- Node selectors to which the VPC Egress Gateway applies.
- Namespace and Pod selectors to which the VPC Egress Gateway applies.
- Policies for the VPC Egress Gateway, including SNAT and subnets/ipBlocks to be applied.
- Whether to enable SNAT for the policy.
- Subnets to which the policy applies.
- IP blocks to which the policy applies.
The above resource creates a VPC Egress Gateway named gateway1 under the default namespace,
and the following Pods will access the external network via the macvlan1 subnet:
- Pods in the default namespace.
- Pods under the subnet1 subnet.
- Pods with IPs in the CIDR 10.18.0.0/16.
NOTICE
Pods matching .spec.selectors will access the external network with SNAT always enabled.
After the creation is complete, check out the VPC Egress Gateway resource:
$ kubectl get veg gateway1
NAME VPC REPLICAS BFD ENABLED EXTERNAL SUBNET PHASE READY AGE
gateway1 ovn-cluster 1 false macvlan1 Completed true 13s
To view more informations:
kubectl get veg gateway1 -o wide
NAME VPC REPLICAS BFD ENABLED EXTERNAL SUBNET PHASE READY INTERNAL IPS EXTERNAL IPS WORKING NODES AGE
gateway1 ovn-cluster 1 false macvlan1 Completed true ["10.16.0.12"] ["172.17.0.11"] ["kube-ovn-worker"] 82s
To view the workload:
$ kubectl get deployment -l ovn.kubernetes.io/vpc-egress-gateway=gateway1
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
gateway1 1/1 1 1 4m40s
$ kubectl get pod -l ovn.kubernetes.io/vpc-egress-gateway=gateway1 -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm 1/1 Running 0 4m48s 10.16.0.12 kube-ovn-worker <none> <none>
To view IP addresses, routes, and iptables rules in the Pod:
$ kubectl exec gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm -c gateway -- ip address show
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: net1@if13: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 62:d8:71:90:7b:86 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.11/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global net1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::60d8:71ff:fe90:7b86/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
17: eth0@if18: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1400 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 36:7c:6b:c7:82:6b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.16.0.12/16 brd 10.16.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::347c:6bff:fec7:826b/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
$ kubectl exec gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm -c gateway -- ip rule show
0: from all lookup local
1001: from all iif eth0 lookup default
1002: from all iif net1 lookup 1000
1003: from 10.16.0.12 iif lo lookup 1000
1004: from 172.17.0.11 iif lo lookup default
32766: from all lookup main
32767: from all lookup default
$ kubectl exec gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm -c gateway -- ip route show
default via 172.17.0.1 dev net1
10.16.0.0/16 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.16.0.12
10.17.0.0/16 via 10.16.0.1 dev eth0
10.18.0.0/16 via 10.16.0.1 dev eth0
172.17.0.0/16 dev net1 proto kernel scope link src 172.17.0.11
$ kubectl exec gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm -c gateway -- ip route show table 1000
default via 10.16.0.1 dev eth0
$ kubectl exec gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm -c gateway -- iptables -t nat -S
-P PREROUTING ACCEPT
-P INPUT ACCEPT
-P OUTPUT ACCEPT
-P POSTROUTING ACCEPT
-N VEG-MASQUERADE
-A PREROUTING -i eth0 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x4000/0x4000
-A POSTROUTING -d 10.18.0.0/16 -j RETURN
-A POSTROUTING -s 10.18.0.0/16 -j RETURN
-A POSTROUTING -j VEG-MASQUERADE
-A VEG-MASQUERADE -j MARK --set-xmark 0x0/0xffffffff
-A VEG-MASQUERADE -j MASQUERADE --random-fully
Capture packets in the Gateway Pod to verify network traffic:
$ kubectl exec -ti gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm -c gateway -- bash
nobody@gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm:/kube-ovn$ tcpdump -i any -nnve icmp and host 172.17.0.1
tcpdump: data link type LINUX_SLL2
tcpdump: listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL2 (Linux cooked v2), snapshot length 262144 bytes
06:50:58.936528 eth0 In ifindex 17 92:26:b8:9e:f2:1c ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 104: (tos 0x0, ttl 63, id 30481, offset 0, flags [DF], proto ICMP (1), length 84)
10.17.0.9 > 172.17.0.1: ICMP echo request, id 37989, seq 0, length 64
06:50:58.936574 net1 Out ifindex 2 62:d8:71:90:7b:86 ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 104: (tos 0x0, ttl 62, id 30481, offset 0, flags [DF], proto ICMP (1), length 84)
172.17.0.11 > 172.17.0.1: ICMP echo request, id 39449, seq 0, length 64
06:50:58.936613 net1 In ifindex 2 02:42:39:79:7f:08 ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 104: (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 26701, offset 0, flags [none], proto ICMP (1), length 84)
172.17.0.1 > 172.17.0.11: ICMP echo reply, id 39449, seq 0, length 64
06:50:58.936621 eth0 Out ifindex 17 36:7c:6b:c7:82:6b ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 104: (tos 0x0, ttl 63, id 26701, offset 0, flags [none], proto ICMP (1), length 84)
172.17.0.1 > 10.17.0.9: ICMP echo reply, id 37989, seq 0, length 64
Routing policies are automatically created on the OVN Logical Router:
$ kubectl ko nbctl lr-policy-list ovn-cluster
Routing Policies
31000 ip4.dst == 10.16.0.0/16 allow
31000 ip4.dst == 10.17.0.0/16 allow
31000 ip4.dst == 100.64.0.0/16 allow
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.2 reroute 100.64.0.4
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.3 reroute 100.64.0.3
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29100 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18.ipv4 reroute 10.16.0.12
29100 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18_ip4 reroute 10.16.0.12
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.control.plane_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.3
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.worker2_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.worker_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.4
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.control.plane_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.3
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.worker2_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.worker_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.4
- Logical Router Policy used by the VPC Egress Gateway to forward traffic from the Pods specified by .spec.policies.
- Logical Router Policy used by the VPC Egress Gateway to forward traffic from the Pods specified by .spec.selectors.
If you need to enable load balancing, modify .spec.replicas as shown in the following example:
$ kubectl scale veg gateway1 --replicas=2
vpcegressgateway.kubeovn.io/gateway1 scaled
$ kubectl get veg gateway1
NAME VPC REPLICAS BFD ENABLED EXTERNAL SUBNET PHASE READY AGE
gateway1 ovn-cluster 2 false macvlan Completed true 39m
$ kubectl get pod -l ovn.kubernetes.io/vpc-egress-gateway=gateway1 -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
gateway1-b9f8b4448-76lhm 1/1 Running 0 40m 10.16.0.12 kube-ovn-worker <none> <none>
gateway1-b9f8b4448-zd4dl 1/1 Running 0 64s 10.16.0.13 kube-ovn-worker2 <none> <none>
$ kubectl ko nbctl lr-policy-list ovn-cluster
Routing Policies
31000 ip4.dst == 10.16.0.0/16 allow
31000 ip4.dst == 10.17.0.0/16 allow
31000 ip4.dst == 100.64.0.0/16 allow
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.2 reroute 100.64.0.4
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.3 reroute 100.64.0.3
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29100 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18.ipv4 reroute 10.16.0.12, 10.16.0.13
29100 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18_ip4 reroute 10.16.0.12, 10.16.0.13
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.control.plane_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.3
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.worker2_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.worker_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.4
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.control.plane_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.3
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.worker2_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.worker_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.4
Enabling BFD-based High Availability
BFD-based high availability relies on the VPC BFD LRP function,
so you need to modify the VPC resource to enable BFD Port.
Here is an example to enable BFD Port for the default VPC:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: Vpc
metadata:
name: ovn-cluster
spec:
bfdPort:
enabled: true
ip: 10.255.255.255
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
- Whether to enable the BFD Port.
- IP address of the BFD Port, which MUST be a valid IP address that does not conflict with ANY other IPs/Subnets.
- Node selector used to select the nodes where the BFD Port is running in Active-Backup mode.
After the BFD Port is enabled, an LRP dedicated to BFD is automatically created on the corresponding OVN Logical Router:
$ kubectl ko nbctl show ovn-cluster
router 0c1d1e8f-4c86-4d96-88b2-c4171c7ff824 (ovn-cluster)
port bfd@ovn-cluster
mac: "8e:51:4b:16:3c:90"
networks: ["10.255.255.255"]
port ovn-cluster-join
mac: "d2:21:17:71:77:70"
networks: ["100.64.0.1/16"]
port ovn-cluster-ovn-default
mac: "d6:a3:f5:31:cd:89"
networks: ["10.16.0.1/16"]
port ovn-cluster-subnet1
mac: "4a:09:aa:96:bb:f5"
networks: ["10.17.0.1/16"]
- BFD Port created on the OVN Logical Router.
After that, set .spec.bfd.enabled to true in VPC Egress Gateway. An example is shown below:
apiVersion: kubeovn.io/v1
kind: VpcEgressGateway
metadata:
name: gateway2
namespace: default
spec:
vpc: ovn-cluster
replicas: 2
internalSubnet: ovn-default
externalSubnet: macvlan1
bfd:
enabled: true
minRX: 100
minTX: 100
multiplier: 5
policies:
- snat: true
ipBlocks:
- 10.18.0.0/16
- VPC to which the Egress Gateway belongs.
- Internal subnet to which the Egress Gateway instances are connected.
- External subnet to which the Egress Gateway instances are connected.
- Whether to enable BFD for the Egress Gateway.
- Minimum receive interval for BFD, in milliseconds.
- Minimum transmit interval for BFD, in milliseconds.
- Multiplier for BFD, which determines the number of missed packets before declaring a failure.
To view VPC Egress Gateway information:
$ kubectl get veg gateway2 -o wide
NAME VPC REPLICAS BFD ENABLED EXTERNAL SUBNET PHASE READY INTERNAL IPS EXTERNAL IPS WORKING NODES AGE
gateway2 vpc1 2 true macvlan Completed true ["10.16.0.102","10.16.0.103"] ["172.17.0.13","172.17.0.14"] ["kube-ovn-worker","kube-ovn-worker2"] 58s
$ kubectl get pod -l ovn.kubernetes.io/vpc-egress-gateway=gateway2 -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
gateway2-fcc6b8b87-8lgvx 1/1 Running 0 2m18s 10.16.0.103 kube-ovn-worker2 <none> <none>
gateway2-fcc6b8b87-wmww6 1/1 Running 0 2m18s 10.16.0.102 kube-ovn-worker <none> <none>
$ kubectl ko nbctl lr-policy-list ovn-cluster
Routing Policies
31000 ip4.dst == 10.16.0.0/16 allow
31000 ip4.dst == 10.17.0.0/16 allow
31000 ip4.dst == 100.64.0.0/16 allow
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.2 reroute 100.64.0.4
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.3 reroute 100.64.0.3
30000 ip4.dst == 172.18.0.4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29100 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18.ipv4 reroute 10.16.0.102, 10.16.0.103 bfd
29100 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18_ip4 reroute 10.16.0.102, 10.16.0.103 bfd
29090 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18.ipv4 drop
29090 ip4.src == $VEG.8ca38ae7da18_ip4 drop
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.control.plane_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.3
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.worker2_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29000 ip4.src == $ovn.default.kube.ovn.worker_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.4
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.control.plane_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.3
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.worker2_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.2
29000 ip4.src == $subnet1.kube.ovn.worker_ip4 reroute 100.64.0.4
$ kubectl ko nbctl list bfd
_uuid : 223ede10-9169-4c7d-9524-a546e24bfab5
detect_mult : 5
dst_ip : "10.16.0.102"
external_ids : {af="4", vendor=kube-ovn, vpc-egress-gateway="default/gateway2"}
logical_port : "bfd@ovn-cluster"
min_rx : 100
min_tx : 100
options : {}
status : up
_uuid : b050c75e-2462-470b-b89c-7bd38889b758
detect_mult : 5
dst_ip : "10.16.0.103"
external_ids : {af="4", vendor=kube-ovn, vpc-egress-gateway="default/gateway2"}
logical_port : "bfd@ovn-cluster"
min_rx : 100
min_tx : 100
options : {}
status : up
To view BFD connections:
$ kubectl exec gateway2-fcc6b8b87-8lgvx -c bfdd -- bfdd-control status
There are 1 sessions:
Session 1
id=1 local=10.16.0.103 (p) remote=10.255.255.255 state=Up
$ kubectl exec gateway2-fcc6b8b87-wmww6 -c bfdd -- bfdd-control status
There are 1 sessions:
Session 1
id=1 local=10.16.0.102 (p) remote=10.255.255.255 state=Up
NOTICE
If all the gateway instances are down, egress traffic to which the VPC Egress Gateway is applied will be dropped.
Configuration Parameters
VPC BFD Port
| Fields | Type | Optional | Default Value | Description | Examples |
|---|
| enabled | boolean | Yes | false | Whether to enable the BFD Port. | true |
| ip | string | No | - | The IP address used by the BFD Port.
Must NOT conflict with other addresses. IPv4, IPv6 and dual-stack are supported. | 169.255.255.255 |
| fdff::1 |
| 169.255.255.255,fdff::1 |
| nodeSelector | matchLabels | object | Yes | - | Label selectors used to select nodes that carries the BFD Port work.
The BFD Port binds an OVN HA Chassis Group of selected nodes and works in Active/Backup mode.
If this field is not specified, Kube-OVN automatically selects up to three nodes.
You can view all OVN HA Chassis Group resources by executing kubectl ko nbctl list ha_chassis_group. | A map of {key,value} pairs. | - |
| matchExpressions | object array | Yes | - | A list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed. | - |
VPC Egress Gateway
| Fields | Type | Optional | Default Value | Description | Examples |
|---|
| vpc | string | Yes | Name of the default VPC (ovn-cluster) | VPC name. | vpc1 |
| replicas | integer/int32 | Yes | 1 | Replicas. | 2 |
| prefix | string | Yes | - | Immutable prefix of the workload deployment name. | veg- |
| image | string | Yes | - | The image used by the workload deployment. | docker.io/kubeovn/kube-ovn:v1
.14.0-debug |
| internalSubnet | string | Yes | Name of the default subnet within the VPC. | Name of the subnet used to access the internal/external network. | subnet1 |
| externalSubnet | No | - | ext1 |
| internalIPs | string array | Yes | - | IP addresses used for accessing the internal/external network. IPv4, IPv6 and dual-stack are supported.
The number of IPs specified must NOT be less than replicas.
It is recommended to set the number to <replicas> + 1 to avoid extreme cases where the Pod is not created properly. | 10.16.0.101
fdff::1
169.255.255.255,fdff::1 |
| externalIPs |
| bfd | enabled | boolean | Yes | false | BFD Configuration. | Whether to enable BFD for the Egress Gateway. | - |
| minRX | integer/int32 | Yes | 1000 | BFD minRX/minTX in milliseconds. | 500 |
| minTX |
| multiplier | integer/int32 | Yes | 3 | BFD multiplier. | 1 |
| policies | snat | boolean | Yes | false | Egress policies. | Whether to enable SNAT/MASQUERADE. | true |
| ipBlocks | string array | Yes | - | IP range segments to which the gateway is applied.
Both IPv4 and IPv6 are supported. | 192.168.0.1 |
| 192.168.0.0/24 |
| fd00::1 |
| fd00::/120 |
| subnets | string array | Yes | - | The VPC subnet name to which the gateway is applied.
IPv4, IPv6 and dual-stack subnets are supported. | subnet1 |
| selectors | namespaceSelector | matchLabels | object | Yes | - | Configure Egress policies by namespace selectors and Pod selectors.
SNAT/MASQUERADE will be applied to the matched Pods. | Namespace selector. An empty label selector matches all namespaces. | A map of {key,value} pairs. | - |
| matchExpressions | object array | Yes | - | A list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed. | - |
| podSelector | matchLabels | object | Yes | - | Pod selector. An empty label selector matches all Pods. | A map of {key,value} pairs. | - |
| matchExpressions | object array | Yes | - | A list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed. | - |
| nodeSelector | matchLabels | object | Yes | - | Node selector used to select nodes that carries the workload deployment.
The workload (Deployment/Pod) will run on the selected nodes. | A map of {key,value} pairs. | - |
| matchExpressions | object array | Yes | - | A list of label selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed. | - |
| matchFields | object array | Yes | - | A list of field selector requirements. The requirements are ANDed. | - |
| trafficPolicy | string | Yes | Cluster | Effective only when BFD is enabled.
Available values: Cluster/Local.
When set to Local, Egress traffic will be redirected to the VPC Egress Gateway instance running on the same node if available.
If the instance is down, Egress traffic will be redirected to other instances. | Local |
Additional resources


