Creating Ingresses
Ingress rules (Kubernetes Ingress) expose HTTP/HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to internal routing (Kubernetes Service), enabling control of external access to computing components.
Create an Ingress to manage the external HTTP/HTTPS access to a Service.
When creating multiple ingresses within the same namespace, different ingresses MUST NOT have the same Domain, Protocol, and Path (i.e., duplicate access points are not allowed).
TOC
Implementation Method
Ingress rules depend on the implementation of the Ingress Controller, which is responsible for listening to changes in Ingress and Service. After a new Ingress is created, when the Ingress Controller receives a request, it matches the forwarding rule from the Ingress and distributes the traffic to the specified internal routes, as shown in the diagram below.
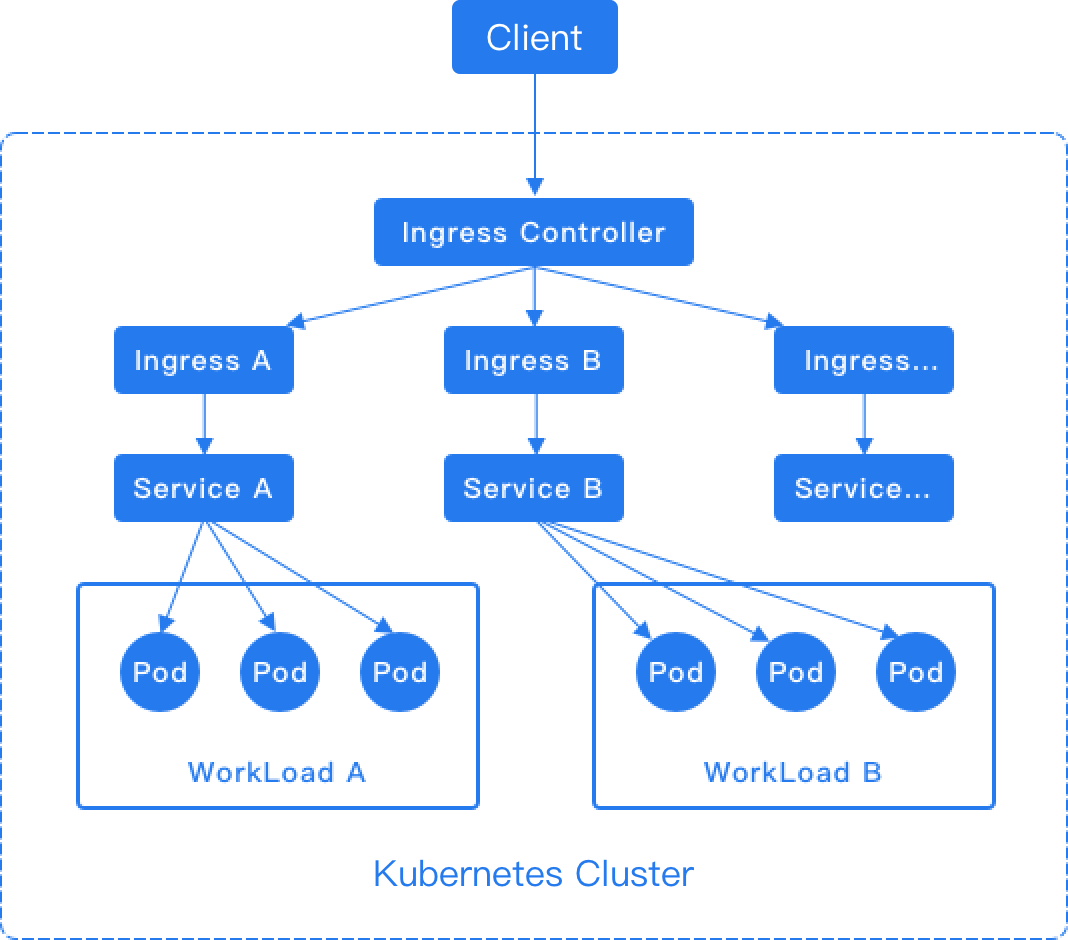
For the HTTP protocol, Ingress only supports the 80 port as the external port. For the HTTPS protocol, Ingress only supports the 443 port as the external port. The platform's load balancer will automatically add the 80 and 443 listening ports.
- install ingress-nginx as ingress-controller via ingress-nginx-operator
- install alb as ingress-controller
Example Ingress:
- To see more configurations please refer to nginx-configuration.
nginxto usingingress-nginxcontroller,$alb_nameto use alb as ingress controller.- If you only want to run ingress locally, configure the
hostsbeforehand.
Creating a Ingress by using the web console
-
Access the Container Platform.
-
In the left navigation bar, click Network > Ingress.
-
Click Create Ingress.
-
Reference the instructions below to configure certain parameters.
Parameter Description Ingress Class Ingresses can be implemented by different controllers with different IngressClassname. If multiple ingress controllers are available on the platform, the user can select which one to use with this option.Domain Name Hosts can be precise matches (for example foo.bar.com) or a wildcard (for example*.foo.com). The domain names available are allocated by platform administrator.Certificates TLS secret or Certificates allocated by platform administrator. Match Type and Path - Prefix: Matches path prefixes, e.g.,
/abcdcan match/abcd/efgor/abcde. - Exact: Matches exact paths, e.g.,
/abcd. - Implementation specific: If you are using a custom Ingress controller to manage the Ingress rules, you may choose to have the controller decide.
Service External traffic will be forwarded to this Service. Service Port Specify which Service port the traffic will be forwarded to. - Prefix: Matches path prefixes, e.g.,
-
Click Create.