Architecture
Reference Document: Zalando Postgres Operator Official Documentation
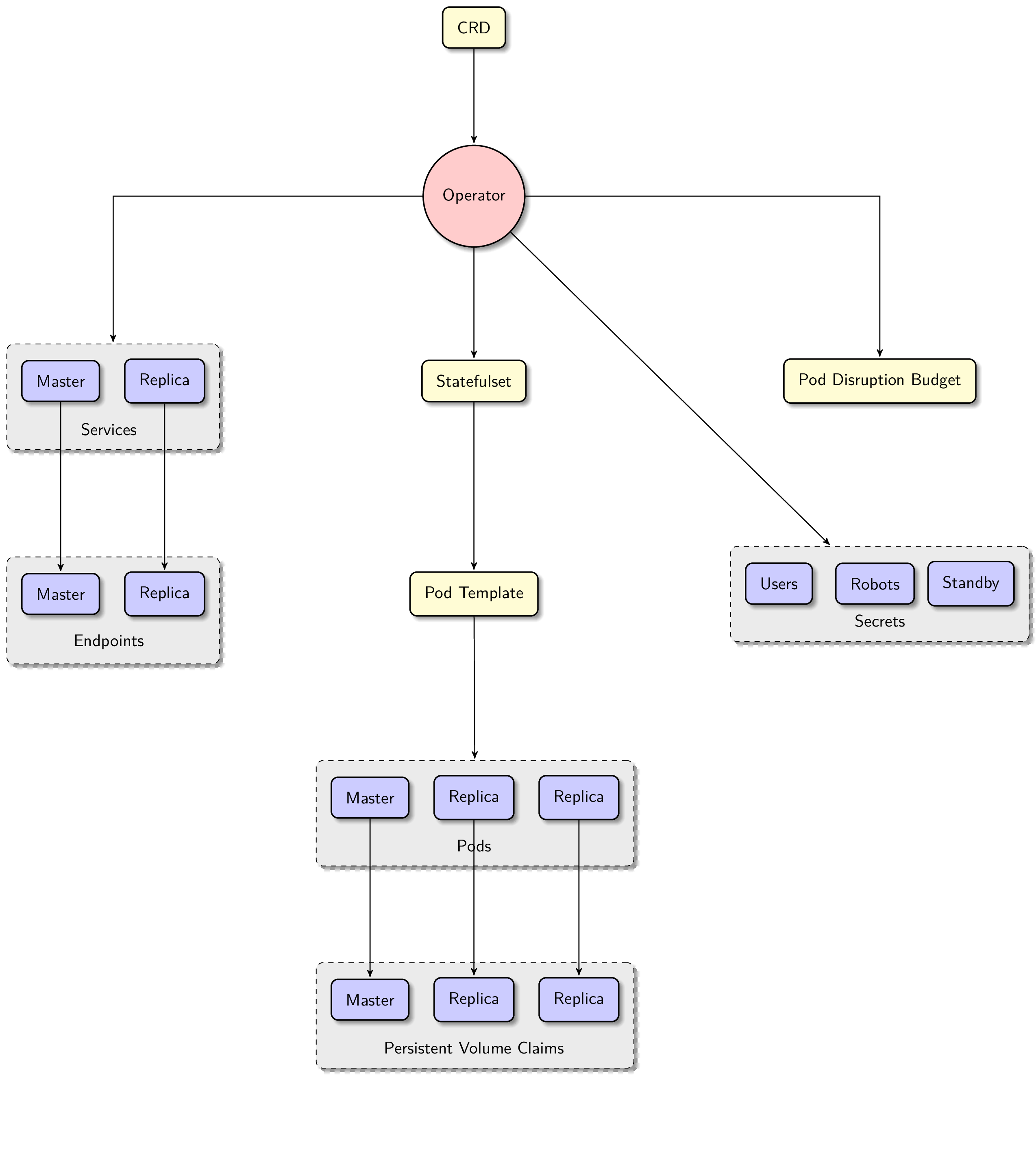
The PostgreSQL Operator manages PostgreSQL clusters using the Kubernetes Operator pattern, primarily consisting of the following core components:
TOC
Core Components
-
Operator Controller
- Listens to changes in PostgreSQL Custom Resource Definitions (CRD)
- Responsible for cluster creation, scaling, configuration updates, and other operations
- Manages the lifecycle of the cluster
-
Patroni
- Provides high availability guarantees
- Handles primary and standby switching and failover
- Manages cluster topology and member status
-
Spilo
- Provides the PostgreSQL container image
- Integrates Patroni and PostgreSQL
- Handles initialization configuration and startup
-
Monitoring Component
- Integrates Prometheus for metrics collection
- Provides Grafana dashboards
- Supports alert rule configuration
Data Flow
- Users create PostgreSQL Custom Resource through the Kubernetes API
- The Operator Controller listens for resource changes and creates the related Kubernetes resources
- Patroni is responsible for the initialization and high availability management of the cluster
- Spilo starts the PostgreSQL instance and applies the configuration
- The monitoring component collects metrics and displays them
Modes
The PostgreSQL Operator supports the following deployment modes:
- Single Cluster Mode: Runs in a single Kubernetes cluster
- Multi-Cluster Mode: Manages PostgreSQL instances across multiple Kubernetes clusters
- High Availability Mode: Achieves automatic failover through Patroni