How to Customize Deployment Templates
TOC
Custom ProcessTemplate StructureBasic InformationUI Dynamic FormDeployment TemplateControl TypesDynamic Form VariablesControl InternationalizationControl Display InformationField ValidationDynamic SelectionFrequently Asked QuestionsHow to access the built-in template content?How to hide the product's built-in template?Custom Process
The custom template process is as follows:
- Configure the template: According to the explanation in the Configure Template section, configure the content of the template as needed
- Register and verify the template: According to the explanation in the Register and Verify the Template section, register the template in the target cluster and verify the template content
Configure Template
Template Structure
The tool deployment template is defined and managed through the ConfigMap resource. Each template consists of the following three main parts:
- Basic information: Contains basic configuration information such as the name, description, and tags of the template
- UI dynamic form: Defines the form items that the user needs to fill in when deploying the tool
- Deployment template: Contains the specific resource definitions required for tool deployment
Basic Information
Basic information includes the template name, description, tags, comments, display name, and description.
Example:
UI Dynamic Form
The tool deployment UI provides dynamic form functionality, which can automatically generate the corresponding form interface according to the form description information in the template, simplifying the user's configuration process.
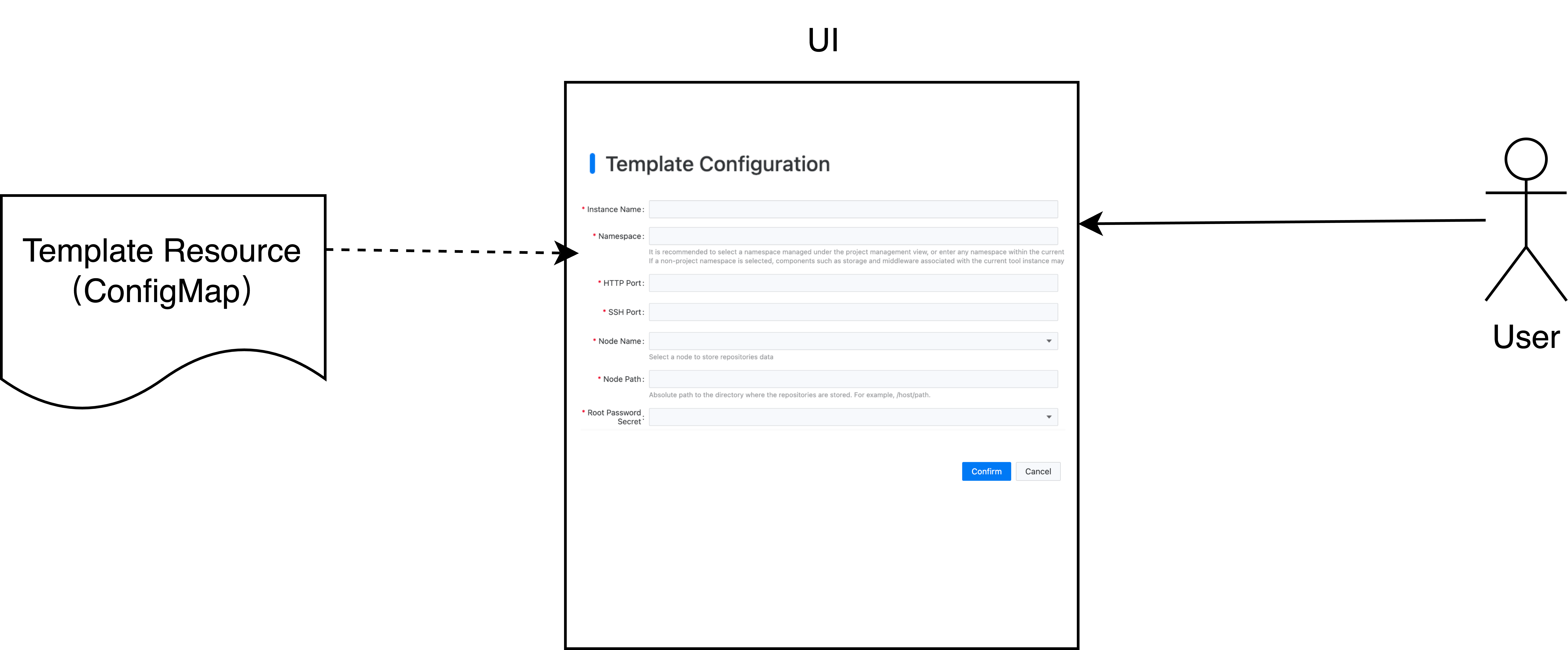
The configuration information of the dynamic form is stored in the ui.cpaas.io/descriptors annotation, the specific format is as follows:
Please refer to the Configure Dynamic Form section for the supported control types of the dynamic form.
Deployment Template
The template engine is implemented based on Helm Template and supports all Helm built-in template functions, such as string processing, mathematical operations, flow control, etc. You can use these functions to build flexible deployment templates.
The main function of the template is to replace the input parameters into the predefined template. The input parameters mainly come from two sources:
- The value entered by the user in the form
- Configuration information obtained from Kubernetes resources.
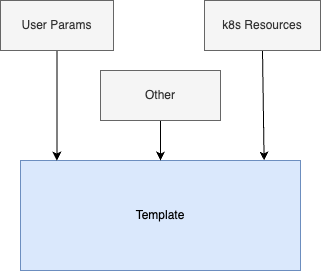
Get parameters from user input
In the template, you can use the {{ .Values.<field name> }} syntax to get the value entered by the user. For example, if a field named domain is defined in the form for entering the deployment domain, then in the template, you can use {{ .Values.domain }} to reference this value.
Get parameters from k8s resources
In the template, you can use the lookup function provided by Helm Template to get configuration information from Kubernetes resources. For example, to get the Redis connection information (such as Host, Port) from the gitlab-redis Secret resource in the tools namespace, you can use the lookup function as follows:
The name of the Secret can also be entered by the user. For example, if a field named redisSecret is defined, you can use .Values.redisSecret to reference the Secret name entered by the user in the template.
Configure Internationalization
The template supports internationalization configuration. When displayed on the UI, the corresponding name and description will be displayed according to the language selected by the user.
The supported internationalization configuration annotations include:
ui.cpaas.io/displayName.<language>ui.cpaas.io/description.<language>ui.cpaas.io/configuration.<language>
To configure internationalization, just add the language code at the end of the field, such as:
zh: Display when Chinese is selecteden: Display when English is selected
Example:
Configure Dynamic Form
Control Types
Common control types include: string, number, and drop-down box.
Example:
Dynamic Form Variables
The following variables can be used when describing the dynamic form:
${context.cluster}: The name of the current cluster${context.namespace}: The current namespace (the namespace where the user selects the tool to be deployed)
Example:
Control Internationalization
The tool deployment template supports configuring the international display content of the control's name, description, and placeholder. By adding descriptors with language codes in the x-descriptors, the system can dynamically display the corresponding text according to the user's language preference.
The supported internationalization configuration types include:
- Control Name (label):
urn:alm:descriptor:label:<language>:<name> - Control Description (description):
urn:alm:descriptor:description:<language>:<description> - Control Placeholder (placeholder):
urn:alm:descriptor:placeholder:<language>:<placeholder>
Where <language> is the language code, currently supported:
zh: Chineseen: English
Example: Configure a domain input box that supports Chinese and English:
Control Display Information
Dynamic form controls support configuring international display content. When displayed on the UI, the corresponding name and description will be displayed according to the user's language selection.

Field Validation
The dynamic form supports validating user input. The supported validation rules are as follows:
Example 1: Limit the value range to: 30000 ~ 32767
Example 2: Limit the string field to be required
Example 3: Limit the path entered by the user to be an absolute path
Example 4: Limit the length of the user input to 2-32 characters
Dynamic Selection
The dynamic form supports dynamically loading the option list by calling the API.
Example: Get the Secret resource from the devops namespace of the test cluster and use metadata.name as the display name and value of the option.
Register and Verify the Template
-
Register the custom template:
- Create the template resource (
ConfigMap) in thecpaas-systemnamespace of the target cluster to complete the registration.
- Create the template resource (
-
Verify the template registration:
- Enter the tool operator details page
- Click the
Create Resourcebutton to enter the template selection page - If you can see the newly added template, the registration is successful
-
Verify the template content:
- Access the tool Operator details page
- Click the
Create Resourcebutton to enter the template selection page - If the newly added template is visible, it indicates successful registration
-
Verify template content:
- Select the custom template
- Follow the interface prompts to create a tool instance
- If the tool instance can be successfully deployed, it indicates that the template content is correct
Frequently Asked Questions
How to access the built-in template content?
After the tool operator is deployed, it will automatically register the built-in deployment templates in the cpaas-system namespace of the current cluster. You can view the template content through the following path:
- Enter the platform
Management View - Select
Cluster Management>Resource Management - Select the resource type as
ConfigMap - Search for the keyword
templateto find the corresponding template
How to hide the product's built-in template?
If you need to hide the product's built-in template, you can add the ui.cpaas.io/hidden label to the template resource and set it to true. Additionally, you need to add the skip-sync annotation; otherwise, the operator will restore the template content when restarting or upgrading.